3D Printing: The Ultimate Guide to Additive Manufacturing
- shiva ganesh
- Jul 31
- 4 min read
Table of Contents
Introduction to 3D Printing
What is 3D Printing?
3D Printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing (AM), is a process of creating three-dimensional solid objects directly from digital models by layering materials. Unlike subtractive methods like CNC machining, 3D printing builds parts layer-by-layer, enabling the creation of complex geometries with minimal waste.
Whether it’s prototyping medical devices, aerospace parts, or architectural models, 3D printing offers unmatched flexibility and customization.
A Brief History of 3D Printing Technology
The roots of 3D printing date back to the 1980s with the invention of stereolithography (SLA). Over the decades, advancements like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) have broadened its applications. Today, 3D printing is revolutionizing industries with rapid prototyping, lightweight components, and even bio-printing.
How 3D Printing Works
The Basic Workflow
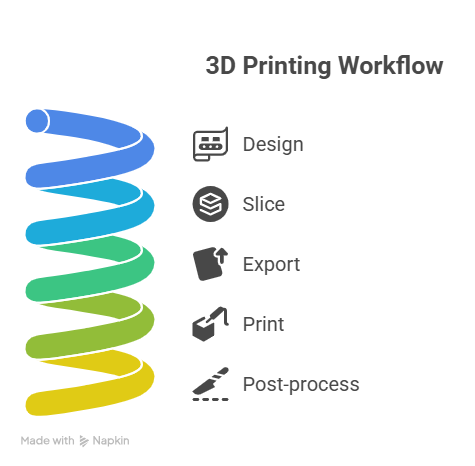
Think of it as assembling something from the ground up, layer by layer:
Design the object using CAD software.
Slice the model into thin layers via slicing software.
Export the file (usually as .STL or .OBJ) and load it into the 3D printer.
Print the object as the printer lays down material layer-by-layer.
Post-process the part (cleaning, curing, smoothing).
Key Components of 3D Printers
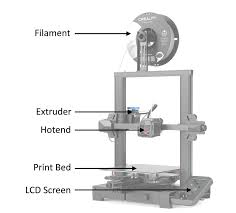
Print Head / Extruder / Laser
The mechanism responsible for depositing or solidifying the material, whether by extruding filament or sintering powder.
Build Platform / Print Bed
The surface where the object is constructed layer by layer.
Control System
Interprets the sliced model and governs movement, temperature, and material flow.
Types of 3D Printers
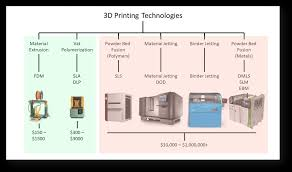
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
The most common type for hobbyists and industry alike. Melts thermoplastic filaments and deposits them layer by layer.
SLA (Stereolithography)
Uses UV light to solidify liquid resin. Known for high accuracy and smooth surfaces.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
Uses lasers to fuse powdered material. Ideal for complex geometries and functional parts.
DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering)
A metal 3D printing process using laser fusion. Widely used in aerospace and medical industries.
Multi-Jet Fusion / PolyJet
Sprays droplets of material and cures them with light. Capable of highly detailed, multi-material prints.
3D Printing Processes

Extrusion-based (FDM)
Melts and extrudes thermoplastic through a nozzle to build objects layer-by-layer.
Vat Photopolymerization (SLA/DLP)
Solidifies resin in a vat using light, layer-by-layer.
Powder Bed Fusion (SLS/DMLS)
Uses heat to fuse powdered materials together selectively.
Material Jetting
Similar to inkjet printing but deposits build and support materials simultaneously.
3D Printing Software

What is Slicing Software?
Slicing software converts 3D CAD models into layer instructions for the printer.
Popular CAD & Slicing Tools:
Fusion 360
SolidWorks
Ultimaker Cura
PrusaSlicer
Autodesk Netfabb
Materials Used in 3D Printing

Polymers
PLA
ABS
PETG
Nylon
TPU (Flexible)
Metals
Stainless Steel
Titanium
Aluminum
Inconel
Resins
Standard Resins
Tough Resins
Dental and Bio-Compatible Resins
Composites
Carbon fiber-reinforced
Glass-filled nylon
Applications of 3D Printing
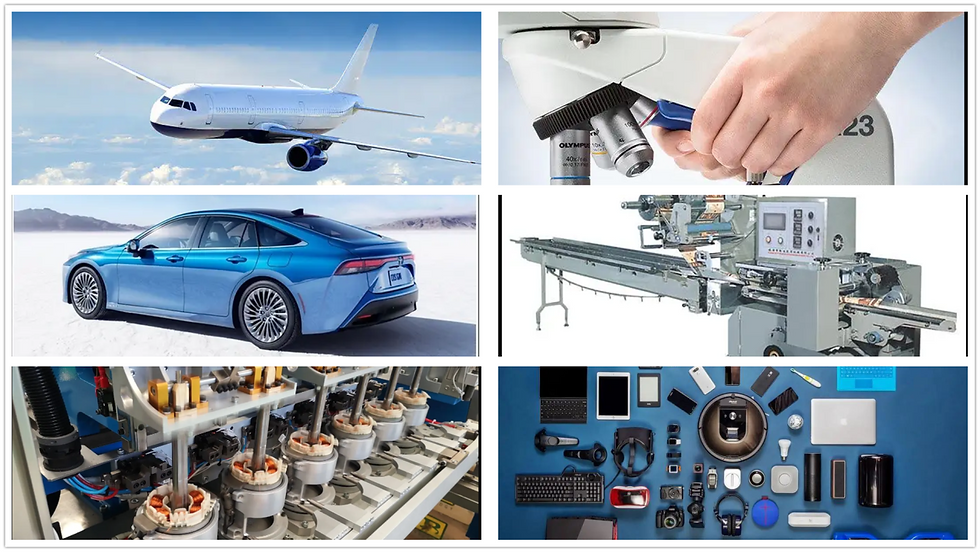

Aerospace
Lightweight, complex geometries for components and tooling.
Automotive
Rapid prototyping, jigs, fixtures, and even end-use parts.
Medical Devices
Custom implants, prosthetics, and surgical planning models.
Consumer Electronics
Casing prototypes, connectors, and lightweight components.
Architecture
Scaled models for visualization and concept presentations.
Advantages of 3D Printing
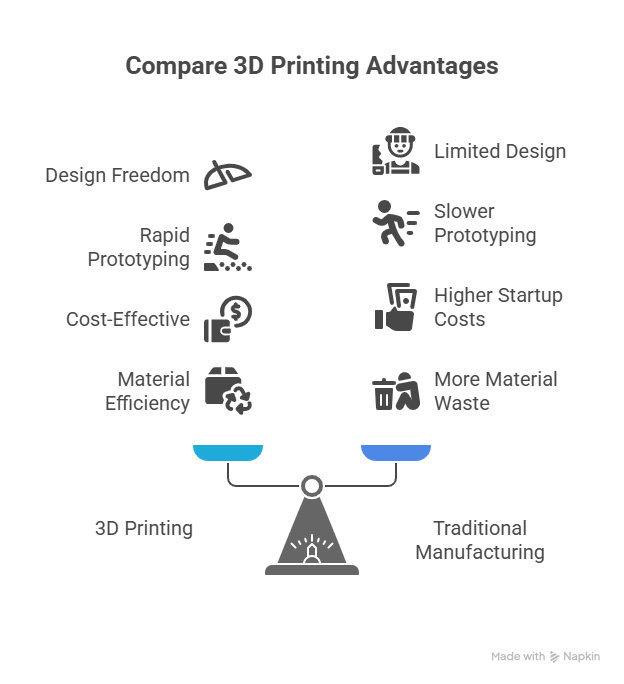
Design Freedom
Create shapes impossible through traditional manufacturing.
Rapid Prototyping
From idea to physical model within hours or days.
Cost-Effective for Low Volumes
No tooling required, reducing startup costs.
Material Efficiency
Minimal waste compared to subtractive methods.
Limitations of 3D Printing

Mechanical Properties
Layer adhesion may result in weaker parts than traditionally manufactured ones.
Surface Finish
Often requires post-processing for smoothness or accuracy.
Speed for Large Parts
Can be slower than CNC or injection molding for large-scale production.
Material Restrictions
Not all materials are suitable for 3D printing.
3D Printing vs. CNC Machining
Key Differences
Feature | 3D Printing | CNC Machining |
Process | Additive | Subtractive |
Ideal Use | Prototypes, Complex Shapes | Functional, Structural Parts |
Material | Mostly Plastics / Some Metals | Mostly Metals |
Speed | Slow per part, fast for iteration | Fast for bulk, slow setup |
When to Choose One Over the Other
3D Printing: Prototyping, intricate designs, small batches.
CNC Machining: Precision, structural integrity, mass production.
Future Trends in 3D Printing

AI & Automation
Automated build farms, AI-generated geometries, and autonomous quality control.
Sustainable Materials
Biodegradable and recyclable materials are on the rise.
Mass Customization
Personalized products at scale through digital manufacturing.
Cost Considerations

Cost of Machines
From ₹30,000 for hobby FDM printers to ₹2 crore+ for industrial metal systems.
Cost of Operation and Maintenance
Includes materials, post-processing tools, software licenses, and maintenance.
Choosing the Right 3D Printer
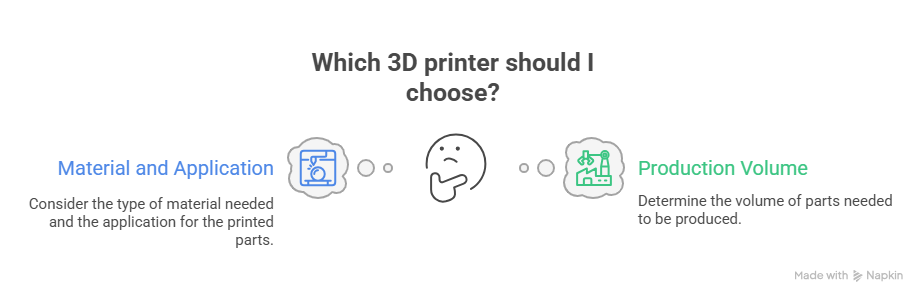
Based on Material and Application
FDM for functional prototypes
SLA for detailed models
SLS/DMLS for production-grade parts
Based on Production Volume
Low volume: Desktop or benchtop
Medium to high volume: Industrial multi-machine setups
Tips for Getting Started with 3D Printing
Training and Certifications
Online platforms: Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning
Manufacturer certifications (Stratasys, EOS, etc.)
Recommended Tools and Resources
YouTube Channels: 3D Printing Nerd, Maker’s Muse
Communities: Reddit r/3Dprinting, Prusa forums
Books: "The 3D Printing Handbook" by 3D Hubs
Conclusion

3D printing is redefining how we design, develop, and manufacture. From rapid prototypes to functional parts, it provides unmatched flexibility and creativity. For startups or large-scale industries, 3D printing opens doors to possibilities once thought impossible




Comments