Plastic 3D Printing: The Ultimate Guide to Additive Manufacturing with Polymers
- shiva ganesh
- Jul 30
- 4 min read
Table of Content

Introduction to Plastic 3D Printing
What is Plastic 3D Printing?

Plastic 3D printing is a type of additive manufacturing that specifically utilizes thermoplastic materials to create parts layer-by-layer from a digital model. It is one of the most accessible and widely used forms of 3D printing, known for rapid prototyping, complex geometries, and cost-effective low-volume production.
A Brief History of Plastic 3D Printing
Plastic 3D printing began with stereolithography (SLA) in the 1980s. The 1990s brought Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), which revolutionized accessibility to 3D printing, particularly for plastics. Over time, material quality and machine precision have evolved, making plastic 3D printing essential for industries from automotive to healthcare.
How Plastic 3D Printing Works
The Basic Workflow

Plastic 3D printing involves the following steps:
Design the model in CAD software.
Slice the model into layers via slicing ``software.
Load the file into the 3D printer.
Print the object by heating and depositing a plastic layer by layer.
Post-process for support removal, surface finish, or painting.
Key Components of Plastic 3D Printers
Extruder / Nozzle (FDM)
Heats and extrudes thermoplastic filament through a small nozzle.
Resin Vat / Light Source (SLA/DLP)
Solidifies liquid resin using UV light layer-by-layer.
Build Platform / Bed
Supports the object as it is printed from the bottom up.
Controller
Operates the printer, following the slicing instructions.
Types of Plastic 3D Printers
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
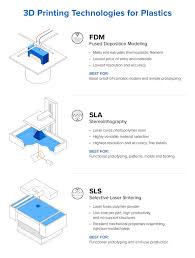
Heats thermoplastic filament and extrudes it in layers. Most common for general-purpose plastic parts.
SLA (Stereolithography)
Uses UV light to cure liquid resin. Ideal for highly detailed, smooth plastic components.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
Fuses powdered thermoplastics with a laser. Suitable for functional prototypes and complex geometries.
PolyJet / Multi-Jet Fusion
Sprays resin droplets cured by light. Allows multi-material and high-detail printing.
Plastic 3D Printing Processes

Extrusion-Based (FDM)
Thermoplastic filament is melted and extruded layer by layer.
Vat Photopolymerization (SLA/DLP)
Liquid resin is solidified by light.
Powder Bed Fusion (SLS)
Thermoplastic powder is selectively fused using heat.
Material Jetting
Sprays and cures photopolymers for detailed parts.
Materials Used in Plastic 3D Printing

Thermoplastics
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
Easy to print, biodegradable, ideal for general prototypes.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Tough, heat-resistant, used in automotive and functional parts.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
Strong, chemically resistant, food-safe.
Nylon (Polyamide)
Durable, flexible, used for gears, hinges, and wear-resistant parts.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
Flexible, rubber-like, used for seals, insoles, and soft-touch parts.
Photopolymers (Resins)
Used in SLA/DLP for high detail and smooth finishes; available in standard, tough, flexible, and dental variants.
Applications of Plastic 3D Printing

Prototyping
Quick iterations of design concepts for review and testing.
Consumer Products
Cases, enclosures, home appliances, and accessories.
Medical
Surgical models, dental appliances, and prosthetic components.
Education
Visual aids, teaching tools, and project prototypes.
Architecture
Scaled models, intricate design elements.
Advantages of Plastic 3D Printing

Cost-Effective Prototyping
Affordable materials and machines for quick design iterations.
Design Flexibility
Complex geometries and organic shapes are easily achievable.
Lightweight Components
Plastic parts are ideal where weight reduction matters.
Material Variety
Wide range of plastics for varied applications.
Limitations of Plastic 3D Printing

Mechanical Strength
Weaker than metals; some plastics may not endure high-stress environments.
Heat Resistance
Most thermoplastics deform at lower temperatures compared to metals.
Surface Finish
May require post-processing for a smooth or aesthetic finish.
Dimensional Accuracy
Warpage and shrinkage can affect precision without proper calibration.
Plastic 3D Printing vs. CNC Machining
Key Differences
Feature | Plastic 3D Printing | CNC Machining |
Process | Additive | Subtractive |
Material | Thermoplastics, Resins | Metals, Plastics |
Cost | Lower for low volume | Higher setup cost |
Speed | Faster for prototypes | Faster for mass production |
Detail | Complex geometries | High-precision parts |
When to Choose One Over the Other
Plastic 3D Printing: Ideal for prototypes, complex shapes, and small runs.
CNC Machining: Ideal for precision, durability, and high-stress applications.
Future Trends in Plastic 3D Printing
Sustainable Materials
Development of biodegradable and recyclable plastics.
Functional Prototypes
Increased use of high-performance plastics for end-use parts.
Automation and AI
Smarter printers, AI-driven slicing, and fully automated print farms.
Cost Considerations
Cost of Machines
₹30,000 to ₹3 lakhs for FDM; ₹2 lakhs to ₹10 lakhs+ for industrial SLA or SLS systems.
Cost of Operation and Maintenance
Includes filaments/resins, regular maintenance, calibration, and software.
Choosing the Right Plastic 3D Printer
Based on Material and Application
FDM: General purpose
SLA: High detail, aesthetics
SLS: Functional prototypes, complex geometries
Based on Production Volume
Hobby / Prototype: Desktop FDM
Small Batch / Functional: SLS / Industrial FDM / SLA
Tips for Getting Started with Plastic 3D Printing
Training and Certifications
Online courses: Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning
Manufacturer certifications: Formlabs, Ultimaker
Recommended Tools and Resources
YouTube: Maker’s Muse, 3D Printing Nerd
Communities: r/3Dprinting, Prusa forums
Books: "The 3D Printing Handbook" by 3D Hubs
Conclusion
Plastic 3D printing democratizes manufacturing, making prototyping and small-scale production affordable and efficient. From educational models to production aids, it brings ideas to life with speed, flexibility, and creativity.





Comments