Sheet Metal Fabrication: The Ultimate Guide to Metal Forming and Manufacturing
- shiva ganesh
- Jul 30
- 4 min read
Table of Content

Introduction to Sheet Metal Fabrication

What is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Sheet Metal Fabrication is a manufacturing process used to create components and structures from flat metal sheets. It involves techniques such as cutting, bending, punching, welding, and assembling to form functional products ranging from small brackets to large enclosures.
Commonly used metals include steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. This process is vital in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, appliances, construction, and industrial equipment.
A Brief History of Sheet Metal Work
The use of sheet metal dates back centuries, with early applications in armor and architectural elements. Modern industrial sheet metal fabrication began in the late 19th century with advancements in press brakes, stamping, and welding technologies. Today, computer-controlled equipment (CNC) ensures precision and efficiency in mass production and prototyping.
How Sheet Metal Fabrication Works

The Basic Workflow
Design the part using CAD software.
Develop a flat pattern considering bends and tolerances.
Cut the flat sheet using lasers, waterjets, or CNC punches.
Form the sheet through bending, stamping, or rolling.
Join parts via welding, riveting, or fasteners.
Finish with coating, painting, or plating as required.
Inspect for dimensional accuracy and quality.
Key Equipment in Sheet Metal Fabrication

Laser Cutters
For precise, clean cuts in a variety of materials and thicknesses.
CNC Turret Punch Press
Performs punching and nibbling operations on sheet metal.
Press Brake
Bends sheet metal to create angles, flanges, and channels.
Roll Formers
Gradually forms sheet metal into cylindrical or curved shapes.
Welding Equipment
Joins metal parts through MIG, TIG, or spot welding.
Hardware Insertion Machines
Installs nuts, studs, and fasteners.
Sheet Metal Fabrication Processes

Cutting
Laser Cutting
Plasma Cutting
Waterjet Cutting
Shearing
Forming
Bending
Rolling
Stamping
Deep Drawing
Joining
Welding (MIG, TIG, Spot)
Riveting
Fastening (hardware insertion)
Finishing
Powder Coating
Anodizing
Painting
Galvanizing
Materials Used in Sheet Metal Fabrication

Common Materials
Steel
Mild steel, galvanized steel, stainless steel.
Aluminum
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
Copper & Brass
For electrical components and decorative purposes.
Titanium
Lightweight, high strength, corrosion-resistant.
Applications of Sheet Metal Fabrication
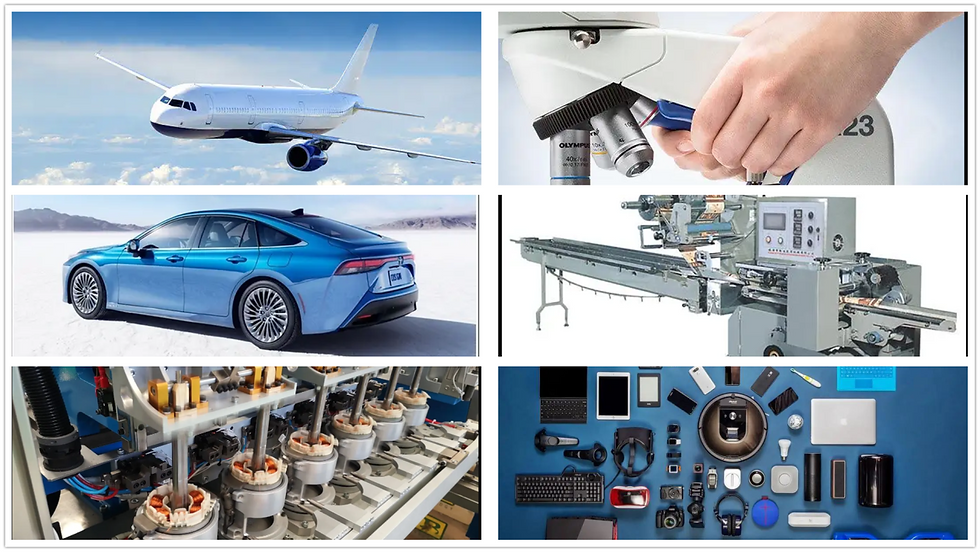

Automotive
Body panels, brackets, chassis components, heat shields.
Aerospace
Structural components, enclosures, ducting.
Electronics
Enclosures, heat sinks, mounting brackets.
Industrial Equipment
Machine guards, conveyor systems, control panels.
Architecture
Facades, roofing, HVAC ductwork.
Appliances
Frames, panels, housings.
Advantages of Sheet Metal Fabrication

Versatility
Suitable for simple to complex parts across industries.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Delivers durable, lightweight solutions.
Scalability
Effective for prototypes and mass production.
Precision
CNC-controlled equipment ensures high accuracy and repeatability.
Material Efficiency
Optimizes material usage with nesting software and advanced cutting techniques.
Limitations of Sheet Metal Fabrication

Thickness Constraints
Typically limited to thin sheets (up to ~6mm).
Tooling Costs
Stamping and deep drawing require expensive tooling for mass production.
Design Restrictions
Sharp bends and small details require design considerations to prevent failure.
Surface Finish Sensitivity
Scratches and marks may require secondary finishing.
Sheet Metal Fabrication vs. Other Manufacturing Processes
Key Differences
Feature | Sheet Metal Fabrication | CNC Machining | 3D Printing |
Material | Sheet metals | Solid blocks | Plastics, metals |
Strength | High | Very High | Moderate |
Complexity | 2D/3D with bending | High complexity | Very high geometry |
Volume | Medium to high | Low to medium | Low to medium |
Speed | Fast (after setup) | Slower for large parts | Slow for production |
When to Choose Sheet Metal Fabrication
For functional, structural components with moderate complexity.
For enclosures, panels, and brackets.
When scalability and durability are key.
Future Trends in Sheet Metal Fabrication

Automation and Robotics
Robotic systems for bending, welding, and handling are streamlining production.
Advanced Materials
Increased use of high-strength steels, composites, and hybrid materials.
Smart Factories
Integration with Industry 4.0 for connected, data-driven manufacturing.
Hybrid Processes
Combining sheet metal with additive manufacturing for complex assemblies.
Cost Considerations

Machine Cost
Laser cutters, press brakes, and punches: ₹20 lakhs to ₹3 crores+.
Operational Costs
Material, tooling, labor, energy.
Secondary processes like finishing and assembly.
Part Cost
Lower per-unit cost for high volumes.
Prototypes and small batches may incur setup charges.
Choosing the Right Sheet Metal Fabrication Setup
Based on Material
Select equipment and techniques suited to steel, aluminum, copper, etc.
Based on Application
Choose processes aligned with strength, finish, and geometry requirements.
Volume Consideration
Prototypes: CNC laser cutting and bending.
Mass Production: Stamping with dedicated tooling.
Tips for Getting Started with Sheet Metal Fabrication
Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Optimize designs to reduce waste, complexity, and costs.
Leverage Software
Use CAD tools like SolidWorks, AutoCAD, Fusion 360 with sheet metal modules.
Understand Tolerances
Account for bend allowances, spring-back, and tool limitations.
Work with Experienced Vendors
Collaborate with fabricators familiar with your industry’s standards.
Conclusion
Sheet Metal Fabrication remains a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering durability, scalability, and precision for countless industries. From simple brackets to complex enclosures, this process delivers efficient solutions for both prototyping and mass production.




Commentaires